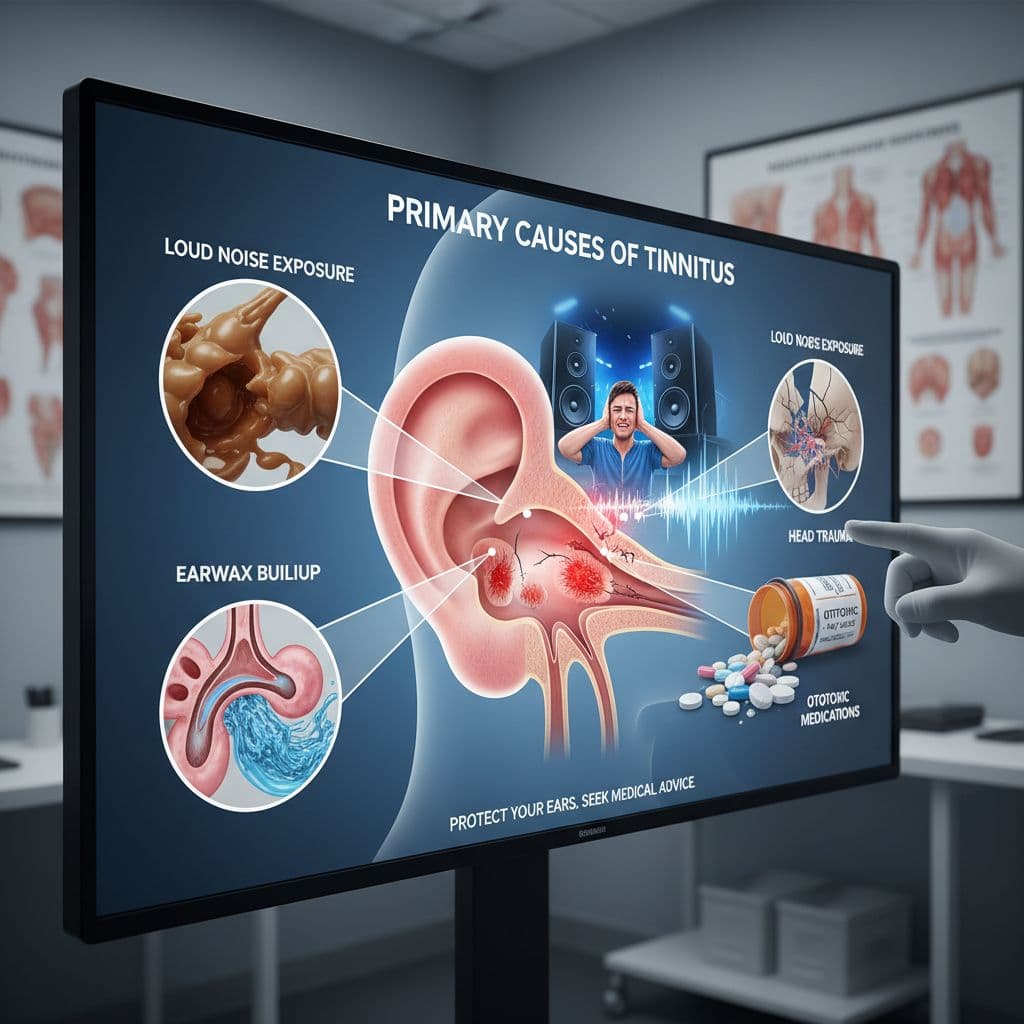
Tinnitus, characterized as the perception of ringing when no external source is present, can be a remarkably troubling condition. Several factors may contribute to its development. Common culprits include exposure to loud music, progressive hearing loss, certain pharmaceuticals, and ear infections. In addition, impacted in the canal can sometimes be a major trigger. Surprisingly, jaw problems (temporomandibular joint dysfunction or TMJ) and even cervical injuries can occasionally provoke tinnitus. Lifestyle choices, such as excessive caffeine consumption or tobacco use, might also exacerbate the condition. Ultimately, identifying the root cause or specific triggers is crucial for appropriate management and possible relief.
The Root of the Ringing: Exploring Tinnitus Etiology
Understanding the origin of tinnitus, that persistent perception of ringing or buzzing in the ears, is a complex undertaking. While often described as simply "ringing in the ears," the condition can manifest in numerous ways, including hissing, clicking, or roaring, and its fundamental causes are surprisingly diverse. From age-related hearing decline and noise-induced damage to ear infections and certain pharmaceuticals, the spectrum of potential causes is broad. Furthermore, sometimes no discernible clinical explanation can be found, leading to what's known as idiopathic tinnitus. Exploring these various reasons is crucial for developing more precise treatments and offering appropriate support to those experiencing this often debilitating affliction. Researchers are diligently working to uncover the neurophysiological processes at play and to ultimately discover ways to lessen the burden of tinnitus for millions worldwide.
Unmasking the Source:Identifying the Cause:Pinpointing the Origin:Exploring the Reasons Behind: Your Tinnitus
While the precise source of tinnitus can be difficult to pinpoint, several common culprits often play a role. Contact to booming noise is a significant factor, frequently stemming from industrial environments, concerts, or even enjoyable activities like firearm use. Specific medications, including ibuprofen and some antibiotics, are also connected to tinnitus. Additional potential triggers involve ear infections, excessive earwax, concussions, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Finally, underlying medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes can sometimes contribute in the development of tinnitus, making a thorough health evaluation vital.
Investigating Tinnitus Causes: From Hearing Loss to Underlying Conditions
The reason for ringing in the ears, commonly known as tinnitus, can be surprisingly varied. While auditory loss, particularly age-related decline, is a frequent contributor – often stemming from damage to the inner ear – it's certainly not the only factor. A variety of other health conditions can also trigger or worsen tinnitus. These include specific head or neck injuries, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, high blood pressure, auditory infections, and even certain drugs. In some instances, tinnitus can be a indication of more complex underlying issues, making a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional vital for proper identification and treatment.
Pinpointing Tinnitus Triggers: A Deep Dive
The persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing associated with tinnitus isn't always a standalone condition; it's frequently a symptom of an hidden issue. Identifying these possible factors is crucial for effective treatment and, in some cases, full relief. Common culprits include acoustic trauma, often from repeated exposure here to loud sounds; certain medications, particularly those with ototoxic properties; impacted earwax, which can physically obstruct the hearing canal; and, less frequently, more serious conditions such as Meniere’s disease or acoustic tumor. Furthermore, habitudinal factors like excessive alcohol consumption or smoking can exacerbate existing hearing issues. A thorough medical evaluation, including audiometry and potentially imaging, is vital to reveal the true origin of your tinnitus and guide appropriate approach.
Acoustic Trauma & Beyond: Investigating Tinnitus Origins
The persistent, often debilitating, ringing or buzzing known as tinnitus ringing isn’t always a straightforward consequence of a single, dramatic event like an explosion. While acoustic trauma traumatic noise exposure certainly remains a key trigger – think concerts, industrial machinery, or military service – a growing body of research suggests a far more complex web of contributing factors. It’s increasingly clear that tinnitus tinnitus can arise from subtle, cumulative noise damage, ototoxic medications medications – pharmaceuticals known to harm the inner ear – temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders disorders, head skull injuries, and even metabolic imbalances. Furthermore, the underlying physiological mechanisms are proving elusive, involving intricate interactions between auditory ear pathways, the brain's auditory cortex, and potentially, the central nervous system’s response to stress stress. Therefore, pinpointing the definitive origin of tinnitus requires a thorough evaluation, often incorporating audiological testing, imaging, and a deep dive into a patient's complete medical medical history – moving far beyond a simple “noise exposure” explanation. The quest to fully understand and effectively treat this pervasive condition demands continued scientific inquiry and a broader perspective.